Androisoxazole
In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of Androisoxazole and all the implications it has on our lives. From its origins to its impact on modern society, we will analyze in detail every relevant aspect related to Androisoxazole. We will discover how Androisoxazole has evolved over time and what its relevance is in today's world. In addition, we will explore the multiple perspectives that exist around Androisoxazole, as well as the controversies and debates it raises. Through this article, we hope to provide a comprehensive and enriching view on Androisoxazole, allowing our readers to better understand this phenomenon and its implications.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Androxan, Neo-Ponden, Neo-Pondus |
| Other names | 17α-Methyl-5α-androstanoisoxazol-17β-ol |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
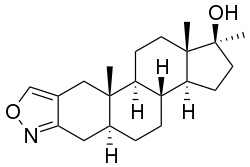
| Formula | C21H31NO2 |
| Molar mass | 329.484 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Androisoxazole (brand names Androxan, Neo-Ponden, Neo-Pondus), also known as 17α-methyl-5α-androstanoisoxazol-17β-ol, is an orally active anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and a 17α-alkylated derivative of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) that is marketed in Spain and Italy. It is closely related to stanozolol, differing only in having an isoxazole instead of pyrazole ring fused to the A ring, and is also related to furazabol, prostanozol, and danazol.
References
- ^ Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 63–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ^ Charles D. Kochakian (6 December 2012). Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 384–. ISBN 978-3-642-66353-6.
- ^ ANTONINI FM, VERDI G (October 1961). "". Minerva Medica (in Italian). 52: 3437–41. PMID 13861810.
- ^ a b ARNOLD A, POTTS GO, BEYLER AL (December 1963). "Relative Oral Anabolic to Androgenic Activity Ratios of Androisoxazole, Ethylestrenol, Methylandrostenolisoxazole and Testosterone". Acta Endocrinologica. 44 (4): 490–8. doi:10.1530/acta.0.0440490. PMID 14082537.